Staking
Prerequisites
In order to submit a staking transaction, you must have the following:
- 2500 EGLD for each node and 0.006 EGLD per node as transaction fee
- A unique
validatorKey.pemfile of each node
You have the option of staking through the online Wallet at https://wallet.elrond.com or by using erdpy.
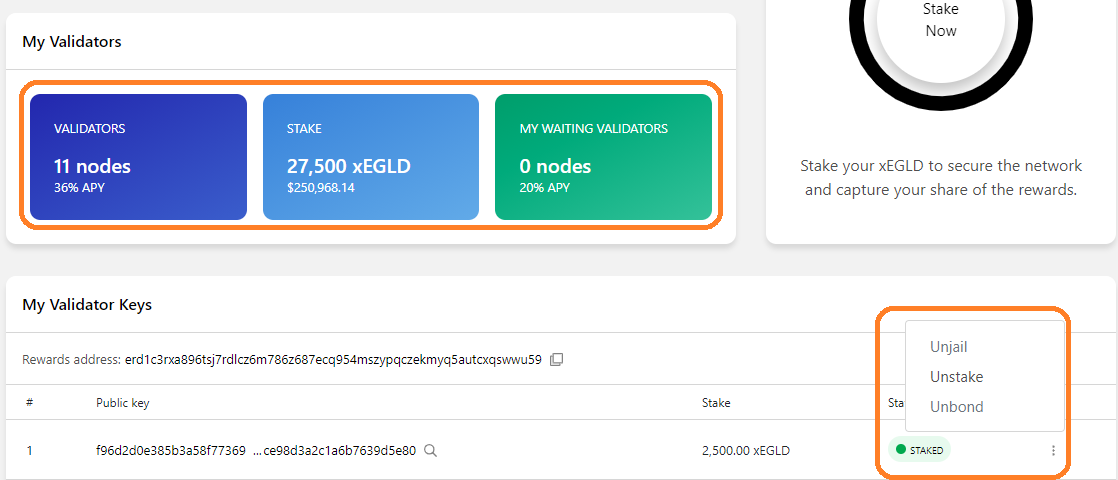
Staking through the Wallet
- Go to https://wallet.elrond.com and log into your wallet
- Go to the Validate section
- Press "Stake now"

- Navigate to the location of the .pem file or drag & drop it
- Press "Continue"
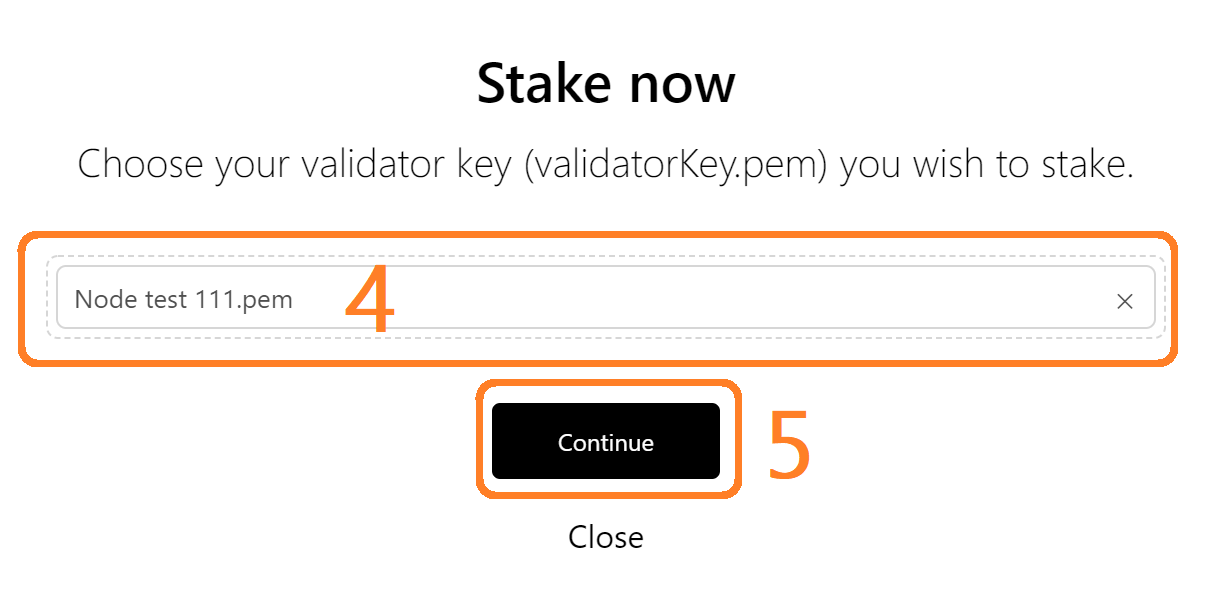
- The staking transaction data is automatically populated using the public key in the .pem certificate you provided. The private key is not touched and the data does not leave your browser. Only the transaction with this public information will be sent to the network once you press Confirm
- Press "Confirm"
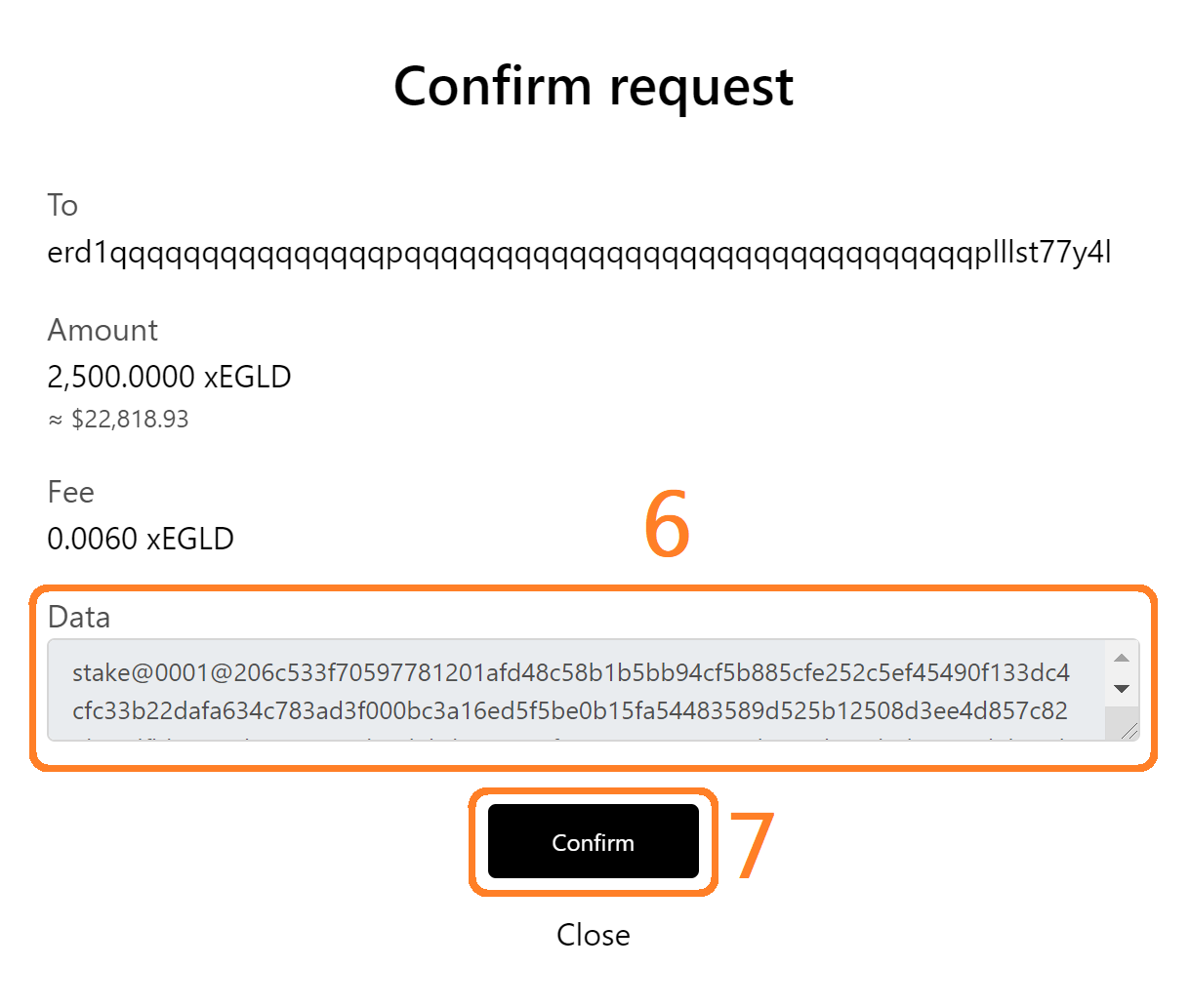
- The status of the transaction will be displayed on screen, together with a success message. Click "Done" once you see the Success message.
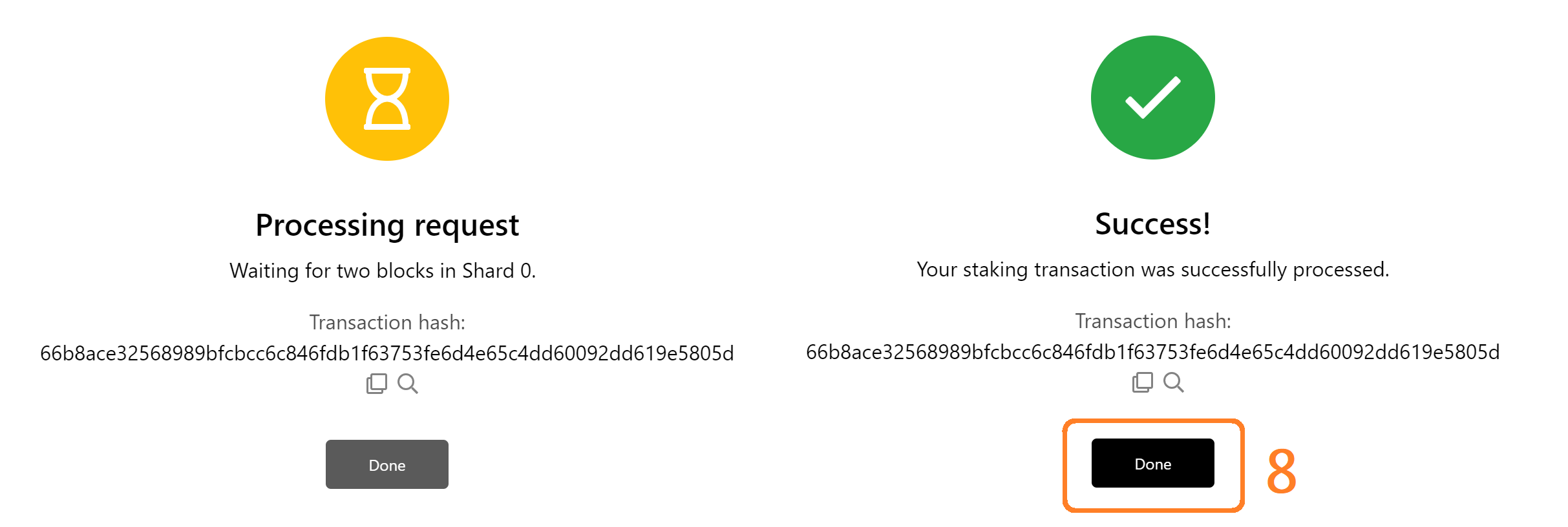
- You can review the transaction in your history. Based on the current staking capacity of the network, you will get an OK message indicating that your node has become a validator, or a response indicating that the network staking is at capacity and your node has been put in the Queue.
- The information about the staked nodes from the current wallet will be updated
- You can further interact with your node(s) by clicking on the three vertical dots next to the public key, which brings up a menu for performing actions such as Unjail, Unstake and Unbond.
Staking through erdpy
Submitting the staking transaction using erdpy avoids having to write the "Data" field manually. Instead, the staking transaction is constructed automatically by erdpy and submitted to the network directly, in a single command.
Make sure erdpy is installed by issuing this command on a terminal:
erdpy --version
The version reported by this command must be at least erdpy 0.8.0, or higher. If erdpy is not installed (command not found), or if the version is lower, please follow these instructions.
Make sure erdpy is installed and has the latest version before continuing.
Your Wallet PEM file
To send transactions on your behalf without using the online Elrond Wallet, erdpy must be able to sign for you. For this reason, you have to generate a PEM file using your Wallet mnemonic.
Please follow the guide Deriving the Wallet PEM file. Make sure you know exactly where the PEM file was generated, because you'll need to reference its path in the erdpy commands.
After the PEM file was generated, you can issue transactions from erdpydirectly.
The staking transaction
The following commands assume that the PEM file for your Wallet was saved with the name walletKey.pem in the current folder, where you are issuing the commands from.
The command to submit a staking transaction with erdpy is this:
erdpy --verbose validator stake --pem=walletKey.pem --value="<stake-value>" --validators-file=<validators-json-file> --proxy=https://gateway.elrond.com --estimate-gas --recall-nonce
Notice that we are using the walletKey.pem file. Moreover, before executing this command, you need to replace the following:
- Replace
<stake-value>with the amount you are staking. You need to calculate this value with respect to the number of nodes you are staking for. See the beginning of the "Staking through the Wallet" section for info on how to do it. - Replace
<validators-json-file>with the JSON file that lists the nodes you are staking for. This JSON file should look like this:
{
"validators" : [
{
"pemFile": "valPem1.pem"
},
{
"pemFile": "valPem2.pem"
},
{
"pemFile": "valPem3.pem"
}
]
}
The pemFile field should point to valid Validator PEM file. Note that paths must be relative to the JSON file itself.
Notice also that there is no calculation for "Gas Limit". If you provide the --estimate-gas argument to erdpy, the gas limit will be estimated automatically.
Here's an example for a staking command for one node:
erdpy --verbose validator stake --pem=walletKey.pem --value="2500000000000000000000" --validators-file=my-validators.json --proxy=https://gateway.elrond.com --estimate-gas --recall-nonce
important
You must take denomination into account when specifying the value parameter in erdpy.
For two nodes, it becomes this:
erdpy --verbose validator stake --pem=walletKey.pem --value="5000000000000000000000" --validators-file=my-validators.json --proxy=https://gateway.elrond.com --estimate-gas --recall-nonce
The --reward-address parameter
When you submit a staking transaction, the Staking SmartContract remembers the wallet you sent it from, and the rewards from your staked validators will go to that wallet. This is the default behavior. In this case, it will be the wallet which you used to generate the walletKey.pem file in the earlier subsection "Your Wallet PEM file".
Alternatively, you can tell erdpy to specify another wallet to which your rewards should be transferred. You will need the address of your reward wallet (it looks like erd1xxxxx…) for this, which you will pass to erdpy using the --reward-address parameter.
For example, a staking command for a single node, with a reward address specified, looks like this:
erdpy --verbose validator stake --pem=walletKey.pem --reward-address="erd1sg4u62lzvgkeu4grnlwn7h2s92rqf8a64z48pl9c7us37ajv9u8qj9w8xg" --value="2500000000000000000000" --number-of-nodes=1 --nodes-public-keys="b617d8bc442bda59510f77e04a1680e8b2d3293c8c4083d94260db96a4d732deaaf9855fa0cef2273f5a67b4f442c725efc06a5d366b9f15a66da9eb8208a09c9ab4066b6b3d38c3cf1ea7fab6489a90713b3b56d87de68c6558c80d7533bf27" --proxy=https://gateway.elrond.com --estimate-gas --recall-nonce
The above command will submit a staking command and will also inform the Staking SmartContract that the rewards should be transferred to the wallet erd1sg4u62lzvgkeu4grnlwn7h2s92rqf8a64z48pl9c7us37ajv9u8qj9w8xg .
